1. Introduction 📚⚖️🕰️
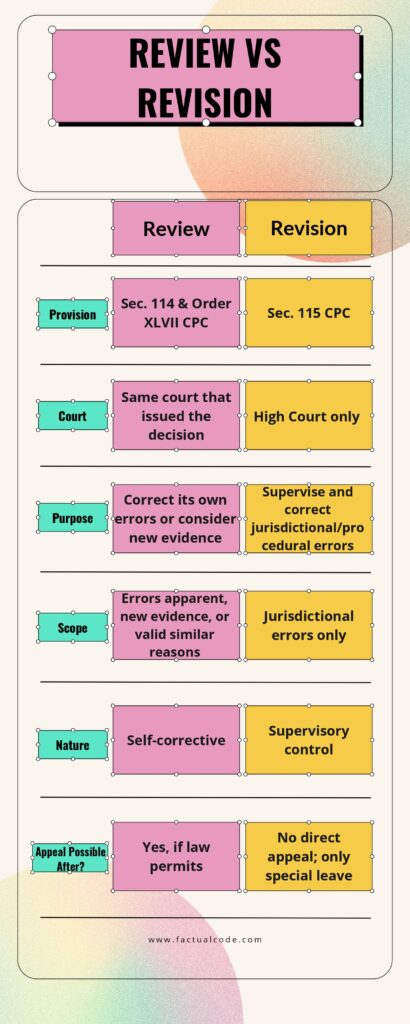
The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 (CPC) is a fundamental law governing the procedures of civil courts in India. Originating during British rule and refined over time, it ensures consistency and fairness in civil justice. Among its many provisions, Review and Revision are vital tools designed to correct mistakes in court decisions. Review empowers the same court that issued a judgment to revisit and correct specific errors, while Revision authorizes the High Court to oversee and correct jurisdictional or procedural errors made by lower courts. These mechanisms safeguard fairness and the integrity of the judicial system. ⚖️✅📜
2. Review under CPC 🔍📖⚖️
Relevant Provisions:
Meaning and Purpose:
A review is the re-examination of a decision by the same court to correct apparent errors or to consider new and important evidence that could not be presented earlier despite due diligence. 🧐⚖️📄
Who Can Apply:
Any party dissatisfied with the judgment or order.
Grounds for Review:
Discovery of new and important facts or evidence not available earlier despite reasonable effort.
An error apparent on the face of the record.
Any other sufficient reason akin to the above.
Nature & Scope:
A review is not an appeal; it is limited to correcting clear mistakes or omissions.
It operates under strict statutory conditions.
Example: If a court overlooks a statutory provision, it may review its own decision. 📜⚖️🔄
Case Law:
Lily Thomas v. Union of India (2000) – Review is meant to correct patent errors, not to reargue the case.
Northern India Caterers v. Lt. Governor of Delhi (1980) – Review is not for altering conclusions without valid grounds. 📚⚖️📝
3. Revision under CPC 🏛️🔎⚖️
Relevant Provision:
Section 115 CPC
Meaning and Purpose:
A revision is the High Court’s supervisory power to examine a lower court’s decision to ensure it acted within its legal authority and followed proper procedure. 🧐🏛️📜
Who Can Apply:
Any party adversely affected by the lower court’s decision.
Grounds for Revision:
The lower court exercised jurisdiction it did not possess.
The lower court failed to exercise jurisdiction it did possess.
The lower court acted illegally or committed a material procedural error.
Nature & Scope:
A revision does not involve re-evaluating evidence; it is limited to jurisdictional or procedural oversight.
It ensures lower courts remain within their legal bounds.
Example: A trial court adjudicates a case exceeding its monetary jurisdiction. ⚖️📋🛑
Case Law:
Major S.S. Khanna v. Brig. F.J. Dillon (1964) – Revision addresses jurisdictional errors, not mere mistakes of law or fact.
Aundal Ammal v. Sadasivan Pillai (1987) – High Court’s revisional authority is confined to the scope of Section 115. 📚⚖️🏛️
5. Conclusion 📝⚖️✅
Review and revision, though similar in purpose, differ in scope and authority. A review is undertaken by the same court to correct its own errors, while a revision is conducted by the High Court to ensure lower courts stay within legal boundaries. Both uphold judicial fairness and prevent the misuse of judicial powers. ⚖️📜🔍
Exam Tip:
Think of it like this — Review = same court + fix errors, Revision = High Court + supervise lower courts. 📚💡✍️

