Introduction
In this article, we are going to talk about all traffic rules in India. The accident rate in India is very high due to overspeeding, bad road conditions, alcohol consumption while driving, lack of street lights, and many more factors. In India, it is common to drive without a helmet or seat belt, and overloading vehicles is frequent. Many of us have received challans (fines) for such violations. With increasing accident rates, it is crucial to follow traffic rules for our safety. Today, we will learn about everything related to traffic challans, rules, regulations, and local RTO guidelines and remedies.
Impact of State Government and Central Government on Traffic Challan
In India, the central government has the power to make rules related to motor vehicles under the Motor Vehicle Act, 1988. State governments also have the authority to modify or implement specific rules within their jurisdictions. These rules cover various aspects of road safety, vehicle registration, licensing, traffic regulation, and traffic challans. Therefore, while the central government can impose new rules and regulations by passing bills, traffic rules may vary across different states.
Motor Vehicle Act, 1988
The Motor Vehicle Act, 1988, encompasses various sections addressing traffic violations and their respective penalties. Some key sections include:
- Section 177: General penalties for offenses not specifically mentioned. Fine: ₹500 for the first offense and ₹1,000 for subsequent offenses.
- Section 199A: Offenses committed by juveniles. Fine: up to ₹25,000.
- Section 180: Allowing unauthorized persons to drive vehicles. Punishment: imprisonment up to 3 months, fine up to ₹5,000, or both.
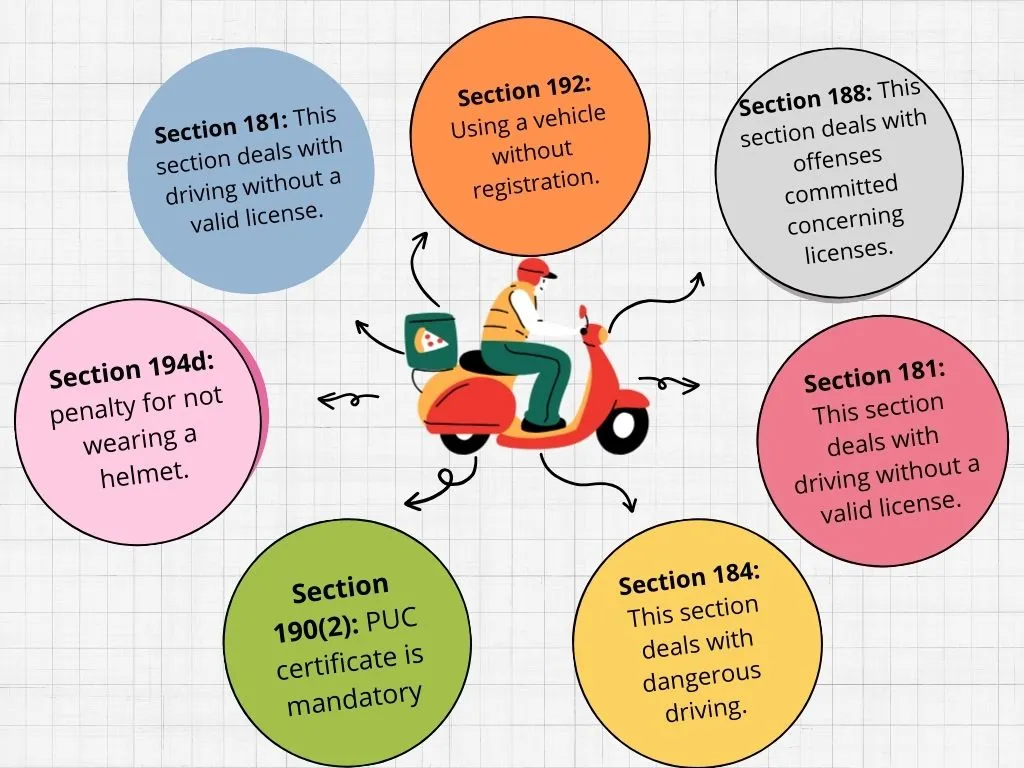
- Section 181: Driving without a valid license. Fine: ₹500 initially, may extend to ₹5,000 and imprisonment up to 3 months.
- Section 183: Driving at an excessive speed. Punishment: fine up to ₹2000.
- Section 184: Dangerous driving. Same punishment as Section 183.
- Section 185: Driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Punishment: 6 months imprisonment and a fine of ₹10,000 for the first offense; 2 years imprisonment and a fine of ₹15,000 for subsequent offenses.
- Section 188: Whoever abets the commission of an offence under section 184, section 185 or section 186 shall be punishable with the punishment provided for the offence.
- Section 190(2): Driving without a PUC certificate. Fine: ₹1,000 for the first offense.
- Section 194c: Violation of protective gear for motorcycle riders and pillion. Fine: ₹1,000 and possible disqualification from holding a license for 3 months.
- Section 194d: Not wearing a helmet. Fine: ₹1,000 and possible disqualification from holding a license for 3 months.
- Section 196: Driving uninsured vehicles. Punishment: 3 months imprisonment and a fine of ₹4,000.
- Section 192: Using a vehicle without registration. Fine: not less than ₹5,000.
- Section 197: Taking out a vehicle without authority. Punishment: imprisonment up to 3 months, fine up to ₹5,000, or both.
- Section 187: Punishment for offenses related to accidents. First offense: imprisonment up to 6 months or fine up to ₹5,000. Subsequent offenses: imprisonment up to 1 year and fine up to ₹10,000.
Role of Local RTO
The local Regional Transport Office (RTO) plays a vital role in vehicle registration, issuing driver’s licenses, and ensuring compliance with road and transport regulations. It handles:
- Vehicle registration
- Driver’s license issuance
- Permit collection and road taxes
- Conducting driving tests
- Managing traffic rules enforcement
The RTO also manages records of vehicles and drivers, promotes road safety and awareness, and helps regulate the overall transport system in its jurisdiction. State governments have the power to impose specific rules in certain areas, leading to variations in traffic enforcement across different regions.
Conclusion
It is crucial to follow traffic rules and norms to reduce the rising number of accidents. To avoid traffic challans, ensure you obey speed limits, use seat belts, signal properly, and avoid using mobile phones while driving. Regular vehicle maintenance and proper documentation can also prevent violations. Stay aware of your surroundings and be cautious, especially in high-traffic areas.
🚗 Road Safety Essentials
For drivers looking to understand their legal responsibilities and rights on the road, we recommend exploring this guide:
- 📌 Navigating Indian Road Accident Laws: A Guide for Drivers - This guide provides a clear overview of what to do after a road accident in India, covering essential legal steps, rights, and responsibilities for drivers.
🚀 Recommended Reading:
For readers interested in understanding the foundational laws that complement traffic regulations, check out our article "Basic Laws in India: A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Legal Essentials" .
🚀 Recommended Reading:
To delve deeper into the evolution of legal systems and their origins, we recommend reading our detailed article "From Ancient Codes to Modern Justice: A Journey Through the Evolution of Law" .