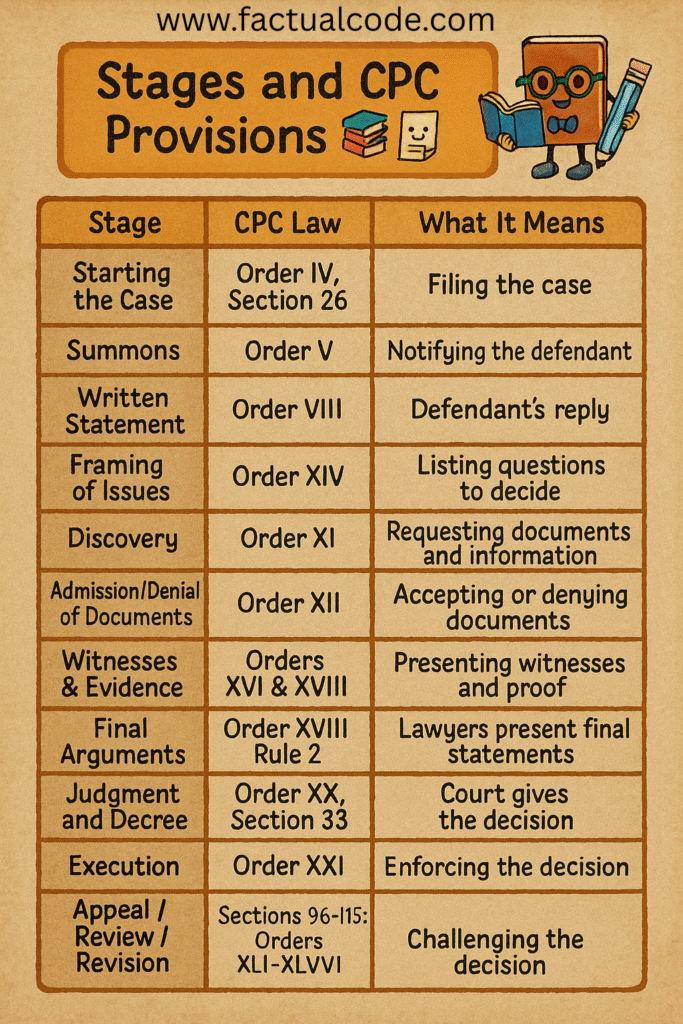
Ever wondered how a civil case works in India? Whether it involves unpaid dues, property issues, or any other private dispute, civil cases follow a step-by-step process to ensure fairness. This guide breaks down the civil suit stages in simple terms so anyone—even if you’re not a law student—can understand.
These steps are described in the Civil Procedure Code, 1908 (CPC), and they’re followed in most courts across India.
Real-Life Example to Help You Understand
Imagine this: Mr. Ramesh, who owns a shop, sells goods worth ₹2,00,000 to Mr. Suresh. But Suresh doesn’t pay him back. After waiting and sending reminders, Ramesh decides to take legal action. He files a civil case to get his money. As we go through each step of the process, we’ll refer back to this example.
1. Filing the Case (Institution of Suit)
This is the first step in the civil case stages. As per Order IV and Section 26 CPC, the person bringing the case (Ramesh) submits a formal complaint (called a “plaint”) to the court. This includes:
- Names of both parties
- A summary of what happened
- Why this court has the authority to hear the case
- What relief is being asked (like payment or an order)
- Proof and documents
Example: Ramesh files his case in court and attaches invoices showing that Suresh owes him money.
2. Court Notifies the Other Side (Summons)
As per Order V CPC, once the case is accepted, the court sends a formal notice (called a summons) to the other person, here Suresh. This tells him about the case and gives him a time limit—usually 30 days—to reply.
Example: Suresh receives the court notice at his home, informing him of the case.
3. Suresh’s Reply (Written Statement)
Under Order VIII CPC, Suresh now files his reply to the case, which is called a “written statement.” He can:
- Agree with some parts
- Deny the claims
- Even make counter-claims
Example: Suresh says he never received the goods, so he doesn’t owe anything.
4. What Are the Key Issues? (Framing of Issues)
Under Order XIV CPC, the judge goes through the plaint and written statement and writes down the main points that need to be decided—called “issues.”
Example:
- Did Suresh actually get the goods?
- Should he pay Ramesh ₹2,00,000?
5. Sharing Documents (Discovery & Inspection)
As per Order XI CPC, both sides can ask each other to show documents and evidence. This helps the court get the full picture.
Example: Ramesh asks to see Suresh’s store records to prove delivery.
6. Agreeing or Disputing Documents
Order XII CPC requires both sides to confirm whether they accept or reject the documents shown by the other party.
Example: Suresh accepts the invoice is signed by him, but says the goods were never delivered.
7. Witnesses and Proof
Under Orders XVI and XVIII CPC, both parties can bring witnesses to court. They give their statements, and then the other side can ask them questions (cross-examination).
Example: Ramesh brings the delivery person to testify. Suresh asks him questions in court.
8. Final Arguments by Lawyers
This is the stage where both lawyers summarize their sides. They explain the evidence, the law, and why the judge should decide in their client’s favor. Order XVIII Rule 2 covers this part.
Example: Ramesh’s lawyer shows all proof of delivery. Suresh’s lawyer tries to show why the documents can’t be trusted.
9. Judge Decides the Case (Judgment and Decree)
Under Order XX and Section 33 CPC, the judge now gives a written decision called a “judgment.” Based on that, a formal order or “decree” is passed.
Example: The court rules in Ramesh’s favor. Suresh is ordered to pay the full amount with interest.
10. Getting the Court’s Order Enforced (Execution)
If Suresh doesn’t pay, Ramesh can go back to the court to enforce the judgment under Order XXI CPC. The court can:
- Seize Suresh’s property
- Order recovery from his bank or job
- In rare cases, order arrest
Example: Ramesh requests the court to take Suresh’s goods to recover the money.
11. Don’t Agree with the Judgment? (Appeal, Review & Revision)
If someone feels the judgment is wrong, they can:
- File an appeal in a higher court (Order XLI)
- Ask the same court to review the case (Order XLVII)
- Request a revision if the court made a legal mistake (Section 115)
Example: Suresh appeals the case, saying the judge misunderstood the facts.
 Final Thoughts
Final Thoughts
Understanding the civil suit stages or civil case stages is important not just for law students, but for anyone who wants to know how the Indian legal system works. These steps help ensure fairness, justice, and clarity in resolving civil disputes.


 Final Thoughts
Final Thoughts