India’s tax system is essential for funding public services, but it is often criticized for being overly complex and difficult to navigate. This article highlights the main issues in India’s tax system and suggests ways to simplify and improve it for the average taxpayer.
1. Overview of the Indian Tax System
India’s taxes are divided into two main categories:
Direct Taxes: These include taxes like:
- Income Tax: Paid by individuals and businesses on their earnings.
- Corporate Tax: Applied to business profits.
- Capital Gains Tax: Charged on profits from selling assets like property or stocks.
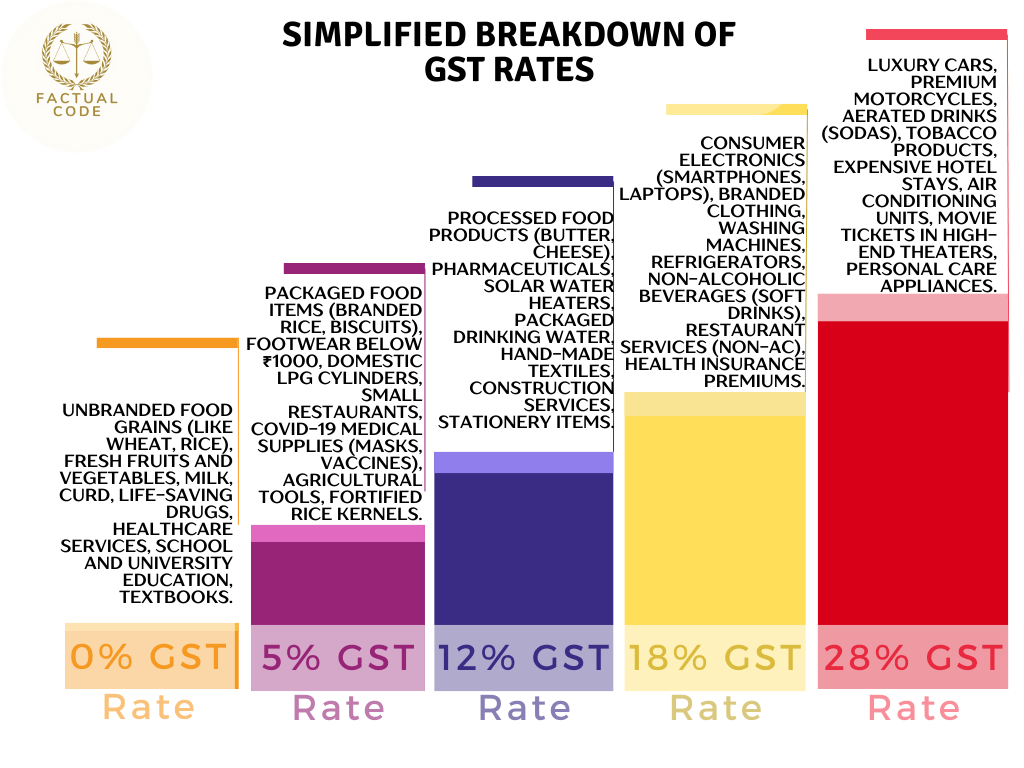
Indirect Taxes: The Goods and Services Tax (GST), which replaced many old taxes, is the main indirect tax. It applies to goods and services, but its multiple rates (0% to 28%) can be confusing. Additionally, luxury items and some other goods are subject to a special tax called the compensation cess.
Although the GST was designed to simplify taxation, its different rates and complex filing requirements have created challenges for businesses, particularly small ones.
2. Complicated Income Tax Rules
Income tax in India is not only progressive (higher earnings attract higher taxes) but also involves various rules for different types of income:
Salary Income: Tax is calculated based on income slabs. Certain exemptions like House Rent Allowance (HRA) or deductions under Section 80C for investments (PPF, insurance, etc.) can lower tax liability, but understanding the rules is often difficult for common taxpayers.
Business Income: Businesses have special deductions like rent and operational costs, but these require detailed bookkeeping and compliance.
Capital Gains: Taxes on gains from assets depend on how long they were held—short-term and long-term gains are taxed differently. For instance, long-term capital gains from shares held over a year are taxed at 10% for gains above ₹1 lakh.
- Other Income: Income from dividends, rental properties, and interest is taxed differently. For instance, interest earned from savings accounts up to ₹10,000 is exempt under Section 80TTA, but this does not extend to interest from fixed or recurring deposits.
Each income source has its own rules, making it complicated for taxpayers to calculate and file their taxes correctly.
3. Deductions and Exemptions
The Indian tax system offers many deductions and exemptions, which can help reduce tax liability, but the conditions attached are complex:
- Section 80C: Deductions up to ₹1.5 lakh are available on specific investments like PPF or life insurance.
- Section 80D: Health insurance premiums are deductible (up to ₹25,000 for individuals and ₹50,000 for senior citizens).
- Section 80E: Education loan interest is deductible, but only for a limited period (up to 8 years).
- HRA and LTA: Employees can reduce taxes by claiming exemptions for rent (HRA) and travel within India (LTA).
Despite being beneficial, the complexity in claiming these exemptions often leaves many taxpayers confused, leading to errors in tax filings or missed opportunities for savings.
4. GST: Simplified but Still Complex
The GST was introduced to unify India’s taxation system, but in practice, its multiple rates and compliance procedures create problems, especially for small businesses:
- Different GST Rates: Goods and services are taxed at various rates (0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, 28%), which creates confusion.
- Compliance Burden: Businesses are required to file regular returns and keep detailed records to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC), which allows them to offset taxes paid on purchases. However, the record-keeping requirements and monthly filings can be burdensome, particularly for small businesses.
Simplifying the rate structure and easing compliance would help smaller businesses better manage their tax obligations.
5. Compliance and Procedural Challenges
Filing tax returns and adhering to procedures remains a challenge:
Return Filing: Despite the availability of online systems, the process can be complicated, leading to mistakes and delays.
Tax Audits and Disputes: Audits can be stressful and often lead to disputes, which are resolved only after lengthy processes. The fear of mistakes or misinterpretations causes anxiety for taxpayers, especially small business owners.
Low Tax Awareness: Many taxpayers lack understanding of their tax responsibilities and the benefits available to them. This often results in incorrect filings or an over-reliance on tax consultants, increasing costs and risks of errors.
6. Areas for Improvement
Several steps could be taken to simplify the tax system:
Reduce GST Slabs: Introducing fewer, more consistent GST rates would make it easier for businesses to comply.
Simplify Deductions and Exemptions: Streamlining the various tax deductions and exemptions into a more straightforward system would reduce confusion for taxpayers.
Expand Digital Education: Increasing awareness and providing simple guides on electronic filing and faceless assessments would help taxpayers understand the system better.
Fast-Track Dispute Resolution: Improving and speeding up the resolution of tax disputes would reduce stress for taxpayers and clear the backlog in the tax system.
Conclusion: Toward a Simpler Tax System
India’s tax system is crucial but burdensome for taxpayers, particularly due to its complex rules, exemptions, and filing procedures. Simplifying tax regulations, improving awareness, and enhancing administrative processes would help make the system more user-friendly, reducing stress and encouraging better compliance.
By focusing on simplification and taxpayer education, India can ensure that its tax system is easier to navigate, fairer, and more efficient, benefiting both individuals and businesses alike.
💡 Recommended Reading
If you're interested in understanding how fiscal policies affect wealth distribution, we suggest reading our detailed post:
- 📌 Rich Get Richer and Poor Get Poorer: Understanding Budget 2024 - Explore how the 2024 budget impacts different income groups, with a focus on the growing gap between the rich and the poor.
📰 Must-Read Insight
Dive into an in-depth analysis of systemic corruption in India with this exposé on the UPSC scam:
🔹 The Puja Khedkar UPSC Scam: A Reflection of Systemic Corruption - Explore the underlying issues and implications of one of India's notable UPSC-related scandals.
📰 Recommended Reading
To further explore how unethical practices disrupt key sectors like education, we recommend reading our in-depth analysis of paper leaks, particularly the NEET paper leak of 2024:
- 📌 Problems of Paper Leaks in India with Special Context of Recent NEET Paper Leak 2024 - Delve into the alarming trend of paper leaks in India, with a focus on its impact on competitive exams like NEET.

